Automotive oem s predominately utilize these parts due to their lower component costs.
Monolithic catalyst vs ceramic honeycomb.
Monolithic ceramics and heterogeneous catalysts.
In the case of honeycombs cordierite is the most commonly applied composition but alternative materials such as sic are beginning to be used for demanding conditions.
Each monolith contains thousands of parallel channels or holes which are defined by many thin walls in a honeycomb structure the channels can be square hexagonal round or other shapes.
The catalyst body typically consists of an extruded ceramic monolith or is made of stacked up or rolled up corrugated sheets of ceramic material or non woven fibers forming a honeycomb monolith with a plurality of parallel gas flow channels.
Many coating companies will suggest ceramic to avoid production.
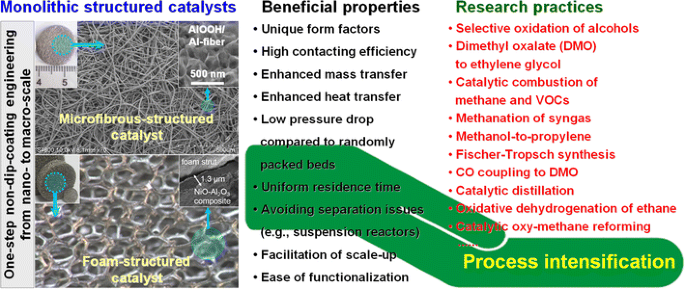
In this paper the current status of the monolith technology for applications in the chemical industry is reviewed.
Exhaust gases flowing through the cells contact the catalyst surface which has been coated onto the cell walls.
For use in gas cleaning the catalyst is impregnated into a washcoat supported on a monolithic substrate.
Catalytic converter with a catalyst coated ceramic honeycomb monolith monolith is a large block of stone or anything that resembles one in appearance intractability etc through which the exhaust gases pass.
Application areas in which monolithic catalysts have superior performance.
Monoliths for automotive catalytic converters are made of a ceramic that contains a large proportion of synthetic cordierite 2mgo 2al 2 o 3 5sio 2 which has a low coefficient of thermal expansion.
Predominately the catalytic converter contains a palladium impregnated ceramic honeycomb monolith then.
Ceramic substrates have been the choice for catalyst coating companies for decades.
Foils used for metal substrates have no porosity.
In the processes of the chemical industry however their current use is very limited.
Honeycombs and foams william m carty and peter w lednor recent advances have been made in research on ceramic monolithic catalyst supports particularly on honeycombs and ceramic foams.
The hydrogen pressure and the temperature were varied between 30 40 bar and 509 523 k respectively.
Engineers prefer metallic coating companies prefer ceramic.
Honeycomb shaped monolithic catalysts are the standard catalyst shape in most environmental applications.
Metallic vs ceramic catalyst substrates.
Recent advances have been made in research on ceramic monolithic catalyst supports particularly on honeycombs and ceramic foams.
Monolithic catalyst substrates compared to materials used in catalysis the walls of ceramic honeycombs have large pores and very low specific surface areas of about 0 3 m 2 g.
Monoliths are sometimes called flow through substrates.